The Baltic States—Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania—stand as beacons of resilience and progress, their unique history and vibrant cultures shaping their present and future. From their geographical location to their political and economic development, the Baltic States offer a captivating narrative that intertwines the past with the present.
Throughout history, the Baltic States have navigated the crossroads of empires, their destiny shaped by the influence of foreign powers. Today, they are thriving democracies, active members of the European Union and NATO, and beacons of regional cooperation.
Historical Context
The Baltic States, comprising Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, have a rich and complex history marked by their strategic location between Eastern and Western Europe. The region has been a crossroads of cultures, trade, and geopolitical interests, leaving an indelible imprint on its development.
The Baltic States emerged as distinct entities during the Middle Ages, with the establishment of the Teutonic Order and the Livonian Confederation. However, their sovereignty was repeatedly challenged by neighboring powers, including Sweden, Poland, and Russia. In the 18th century, the region fell under the control of the Russian Empire, which implemented policies of Russification and suppression of local cultures.
Foreign Influence
Throughout history, the Baltic States have been subjected to significant foreign influence. The Teutonic Order, a German military and religious order, played a major role in shaping the region’s political and cultural landscape. The Livonian Confederation, a loose alliance of German-ruled territories, further cemented German influence in the area.
The Russian Empire’s annexation of the Baltic States in the 18th century had a profound impact on the region. Russian policies of Russification aimed to suppress local languages, cultures, and political institutions. This led to resentment and resistance among the Baltic peoples, who sought to preserve their distinct identities.
In the 20th century, the Baltic States briefly gained independence after the collapse of the Russian Empire. However, they were again occupied by the Soviet Union during World War II. The Soviet era was characterized by economic stagnation, political repression, and the suppression of national identities.
The Baltic States regained their independence in 1991, following the collapse of the Soviet Union. Since then, they have embarked on a path of economic and political development, joining the European Union and NATO. However, the region’s history continues to shape its present-day challenges, including issues of national identity, economic disparities, and geopolitical tensions.
Geography and Demographics
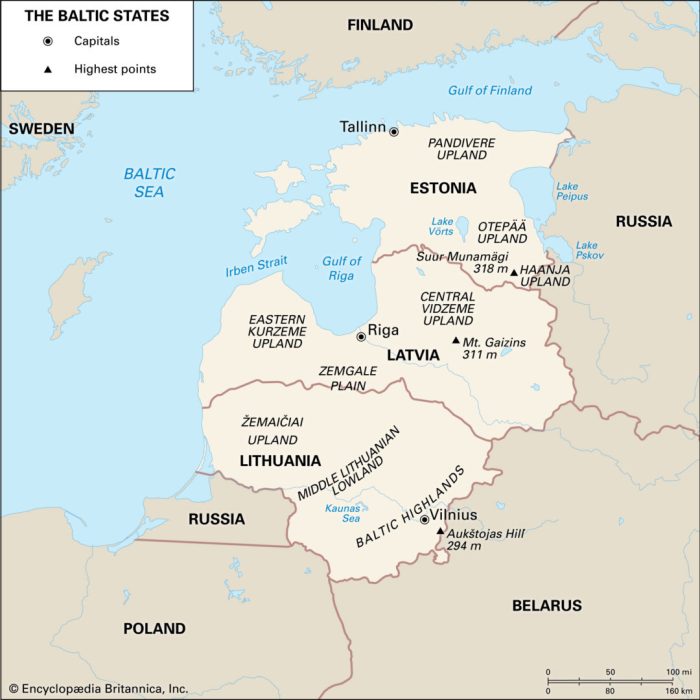
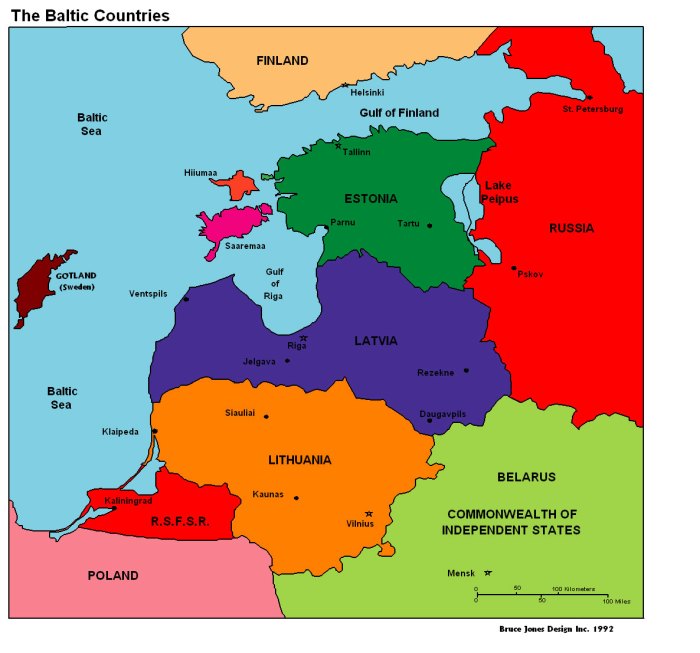
The Baltic States, comprising Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, are situated on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea, nestled between Scandinavia and Russia. This region boasts a diverse landscape characterized by rolling hills, vast forests, and picturesque coastlines.
Geographical Features, Baltic states
Estonia, the northernmost of the Baltic States, is known for its numerous islands, including Saaremaa and Hiiumaa. Its landscape is dominated by forests, wetlands, and limestone outcrops. Latvia, the central Baltic State, features a flat and fertile plain in the west and a hilly region in the east. Lithuania, the southernmost of the trio, is renowned for its rolling hills, lush forests, and numerous lakes.
The Baltic states, with their rich history and stunning landscapes, offer a captivating travel experience. However, if you’re seeking a vibrant coastal escape, consider exploring the sun-kissed shores of Alicante , Spain. From its pristine beaches to its charming old town, Alicante offers a delightful blend of relaxation and cultural immersion.
Yet, the allure of the Baltic states remains strong, inviting you to discover their enigmatic charm and historical treasures.
Population and Demographics
The Baltic States have a combined population of approximately 6 million people. Estonia is the least populous with around 1.3 million inhabitants, followed by Latvia with 1.9 million, and Lithuania with 2.8 million. The majority of the population in all three countries is ethnically Baltic, with Estonians, Latvians, and Lithuanians forming the largest groups, respectively. Russian minorities are also present, particularly in Estonia and Latvia.
Languages and Culture
The Baltic States are linguistically and culturally diverse. Estonian, Latvian, and Lithuanian are the official languages of their respective countries and belong to the Baltic branch of the Indo-European language family. Russian is widely spoken as a second language, especially in urban areas. The region has a rich cultural heritage, influenced by both Western and Eastern European traditions. Estonia is known for its vibrant choral tradition, Latvia for its folk songs and dances, and Lithuania for its historical architecture and cuisine.
Political and Economic Development
The Baltic States have undergone significant political and economic transformations since regaining their independence in 1991. They have established democratic systems, joined international organizations like the European Union and NATO, and experienced rapid economic growth.
The political systems in the Baltic States are characterized by parliamentary democracies with multi-party systems. Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania have all adopted constitutions that guarantee fundamental rights and freedoms. They have also implemented electoral systems that ensure fair and transparent elections.
Economic Development and Growth Patterns
The Baltic States have experienced impressive economic growth since independence. They have transitioned from centrally planned economies to market economies and integrated themselves into the global economy. The region has benefited from foreign investment, trade, and EU membership.
The Baltic States have adopted neoliberal economic policies, emphasizing privatization, deregulation, and free trade. These policies have contributed to economic growth but have also led to challenges such as income inequality and social disparities.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Global Economy
The Baltic States face several challenges and opportunities in the global economy. These include:
- Economic Diversification: The Baltic States have relatively narrow economic bases, relying heavily on exports of goods and services. They need to diversify their economies to reduce vulnerability to external shocks.
- Labor Shortages: The Baltic States have experienced population decline and aging, leading to labor shortages. They need to address this issue through immigration and workforce development.
- Innovation and Competitiveness: The Baltic States need to invest in innovation and research and development to enhance their competitiveness in the global economy.
- Geopolitical Risks: The Baltic States’ proximity to Russia creates geopolitical risks. They need to strengthen their defense capabilities and foster cooperation with NATO and the EU.
Regional Cooperation and Integration
The Baltic States of Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania have actively engaged in regional organizations to enhance their security, economic development, and political influence.
Role in the European Union
The Baltic States joined the European Union (EU) in 2004. Membership in the EU has provided them with economic benefits, including access to the single market, increased trade and investment, and financial assistance. The EU has also supported the Baltic States’ political and institutional development, promoting democracy, human rights, and the rule of law.
Role in NATO
The Baltic States joined the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) in 2004. NATO membership has strengthened their defense capabilities and provided them with security guarantees from the United States and other Western allies. NATO has also played a role in promoting regional stability and deterring potential threats from Russia.
Challenges and Benefits of Regional Cooperation
Regional cooperation offers several benefits for the Baltic States, including:
- Increased economic integration and growth
- Enhanced security and defense capabilities
- Greater political influence and representation
- Improved coordination on common issues
However, regional cooperation also poses some challenges:
- Differences in economic development and interests
- Potential for political disputes or tensions
- Balancing national sovereignty with regional commitments
Successful Regional Initiatives and Collaborations
The Baltic States have collaborated on various regional initiatives, including:
- The Baltic Assembly, a parliamentary forum for cooperation and dialogue
- The Council of the Baltic Sea States, a regional organization promoting cooperation in the Baltic Sea region
- The Nordic-Baltic Eight, a group of eight countries from the Nordic and Baltic regions that collaborate on various issues
These initiatives have facilitated regional cooperation in areas such as trade, energy, infrastructure, and environmental protection.
Cultural Heritage and Identity
The Baltic States of Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania share a rich and diverse cultural heritage shaped by centuries of history, geography, and religion. Each country possesses unique traditions, customs, and folklore that reflect its distinct identity.
After an exhilarating trip to the captivating Baltic states, consider extending your adventure to Adventure Island Tampa , an enchanting waterpark nestled in the heart of Florida. Dive into a realm of thrilling slides, refreshing pools, and adrenaline-pumping attractions, before returning to the serene landscapes and rich history of the Baltic region.
The region’s history has played a significant role in its cultural development. From ancient times, the Baltic States have been influenced by various cultures, including Viking, German, Russian, and Polish. These influences have left an imprint on the region’s architecture, music, and literature.
The Baltic states, comprising Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, boast a rich history and culture. While exploring these captivating countries, consider venturing beyond their borders to witness the architectural marvel that is the Allianz Arena in Munich, Germany. Its innovative design and cutting-edge technology make it a must-visit destination for sports enthusiasts and architecture aficionados alike.
Upon returning to the Baltic states, immerse yourself once more in their enchanting landscapes and vibrant cities.
Geography and Cultural Heritage
The geography of the Baltic States has also shaped its cultural identity. The region’s location on the Baltic Sea has fostered maritime traditions, fishing, and shipbuilding. The vast forests and lakes have influenced the development of forestry, hunting, and nature-based activities.
Religion and Cultural Heritage
Religion has played a significant role in Baltic culture. Christianity arrived in the region in the Middle Ages, and its influence is evident in the numerous churches, cathedrals, and monasteries found throughout the Baltic States. However, traditional pagan beliefs and practices have also persisted, contributing to the region’s unique cultural tapestry.
Preservation and Promotion of Baltic Culture
In recent decades, there has been a growing effort to preserve and promote Baltic culture and traditions. Governments, cultural organizations, and individuals have worked to revitalize traditional crafts, music, dance, and folklore. Festivals and events are held throughout the year to showcase the region’s cultural heritage and foster a sense of national pride.
Environmental Issues and Sustainability
The Baltic States face a range of environmental challenges, including climate change, pollution, and natural resource management. These issues have significant impacts on the region’s ecosystems, human health, and economic development.
Climate Change
Climate change is a major threat to the Baltic States. The region is experiencing rising temperatures, increased precipitation, and more frequent extreme weather events. These changes are already having a negative impact on the region’s ecosystems, agriculture, and infrastructure.
- Rising sea levels are threatening coastal communities and infrastructure.
- Increased flooding is damaging crops and property.
- Heat waves are increasing the risk of wildfires and heat-related illnesses.
Pollution
Pollution is another major environmental challenge facing the Baltic States. The region’s air, water, and soil are all polluted by a variety of sources, including industrial activities, agriculture, and transportation.
- Air pollution is a major problem in urban areas, particularly during the winter months.
- Water pollution is a threat to the region’s lakes, rivers, and coastal waters.
- Soil pollution is a problem in areas where there is intensive agriculture or industrial activity.
Natural Resource Management
The Baltic States are rich in natural resources, including forests, minerals, and water. However, these resources are not always managed sustainably.
- Deforestation is a problem in some areas, particularly in Estonia.
- Overfishing is a threat to the region’s fish stocks.
- Mining can damage the environment and pollute water resources.
Sustainable Practices and Initiatives
The Baltic States are taking steps to address their environmental challenges. A number of sustainable practices and initiatives are being implemented, including:
- Renewable energy: The Baltic States are investing in renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power.
- Energy efficiency: The region is implementing energy efficiency measures in buildings and transportation.
- Waste reduction: The Baltic States are working to reduce waste production and promote recycling.
- Sustainable agriculture: The region is promoting sustainable agricultural practices, such as organic farming and agroforestry.
Outcome Summary
As we conclude our exploration of the Baltic States, it is evident that these nations are not merely a footnote in history but rather a testament to the indomitable spirit of their people. Their journey continues, marked by a commitment to preserving their cultural heritage, fostering economic growth, and playing an active role on the global stage. The Baltic States stand as an inspiration, demonstrating the power of unity, resilience, and the pursuit of a brighter future.
FAQ Summary: Baltic States
What is the historical significance of the Baltic States?
The Baltic States have a rich history, marked by centuries of foreign rule and the struggle for independence. They have been influenced by various empires, including the Russian Empire, the Swedish Empire, and the German Empire.
What is the geographical location of the Baltic States?
The Baltic States are located on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea. They border Russia to the east, Belarus to the south, and Poland to the southwest.
What is the cultural diversity of the Baltic States?
The Baltic States are home to a diverse range of cultures and languages. The official languages are Estonian, Latvian, and Lithuanian, but Russian and other minority languages are also spoken.